Page 235 - Ebook HTKH 2024
P. 235
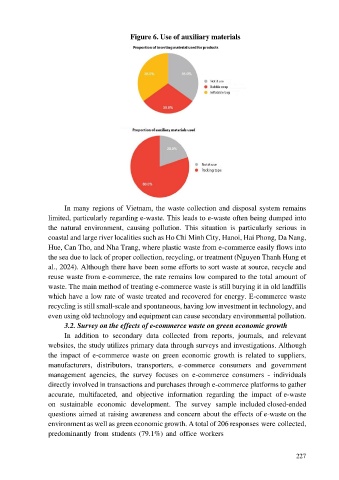
Figure 6. Use of auxiliary materials
In many regions of Vietnam, the waste collection and disposal system remains
limited, particularly regarding e-waste. This leads to e-waste often being dumped into
the natural environment, causing pollution. This situation is particularly serious in
coastal and large river localities such as Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, Hai Phong, Da Nang,
Hue, Can Tho, and Nha Trang, where plastic waste from e-commerce easily flows into
the sea due to lack of proper collection, recycling, or treatment (Nguyen Thanh Hung et
al., 2024). Although there have been some efforts to sort waste at source, recycle and
reuse waste from e-commerce, the rate remains low compared to the total amount of
waste. The main method of treating e-commerce waste is still burying it in old landfills
which have a low rate of waste treated and recovered for energy. E-commerce waste
recycling is still small-scale and spontaneous, having low investment in technology, and
even using old technology and equipment can cause secondary environmental pollution.
3.2. Survey on the effects of e-commerce waste on green economic growth
In addition to secondary data collected from reports, journals, and relevant
websites, the study utilizes primary data through surveys and investigations. Although
the impact of e-commerce waste on green economic growth is related to suppliers,
manufacturers, distributors, transporters, e-commerce consumers and government
management agencies, the survey focuses on e-commerce consumers - individuals
directly involved in transactions and purchases through e-commerce platforms to gather
accurate, multifaceted, and objective information regarding the impact of e-waste
on sustainable economic development. The survey sample included closed-ended
questions aimed at raising awareness and concern about the effects of e-waste on the
environment as well as green economic growth. A total of 206 responses were collected,
predominantly from students (79.1%) and office workers
227