Page 62 - Demo
P. 62
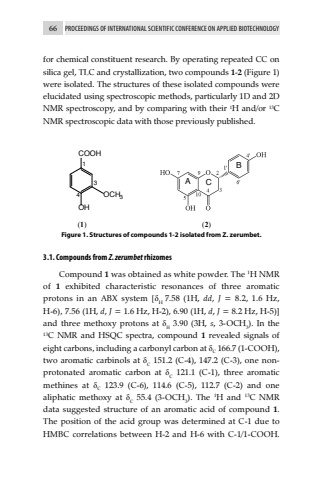
66 PROCEEDINGS OF INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE ON APPLIED BIOTECHNOLOGYfor chemical constituent research. By operating repeated CC on silica gel, TLC and crystallization, two compounds 1-2 (Figure 1) were isolated. The structures of these isolated compounds were elucidated using spectroscopic methods, particularly 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, and by comparing with their 1H and/or 13C NMR spectroscopic data with those previously published.COOHOHOCH3134 (1)ABC (2)Figure 1. Structures of compounds 1-2 isolated from Z. zerumbet.3.1. Compounds from Z. zerumbet rhizomesCompound 1 was obtained as white powder. The 1H NMR of 1 exhibited characteristic resonances of three aromatic protons in an ABX system [%u03b4H 7.58 (1H, dd, J = 8.2, 1.6 Hz, H-6), 7.56 (1H, d, J = 1.6 Hz, H-2), 6.90 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-5)] and three methoxy protons at %u03b4H 3.90 (3H, s, 3-OCH3). In the 13C NMR and HSQC spectra, compound 1 revealed signals of eight carbons, including a carbonyl carbon at %u03b4C 166.7 (1-COOH), two aromatic carbinols at %u03b4C 151.2 (C-4), 147.2 (C-3), one nonprotonated aromatic carbon at %u03b4C 121.1 (C-1), three aromatic methines at %u03b4C 123.9 (C-6), 114.6 (C-5), 112.7 (C-2) and one aliphatic methoxy at %u03b4C 55.4 (3-OCH3). The 1H and 13C NMR data suggested structure of an aromatic acid of compound 1. The position of the acid group was determined at C-1 due to HMBC correlations between H-2 and H-6 with C-1/1-COOH.