Page 65 - Demo
P. 65
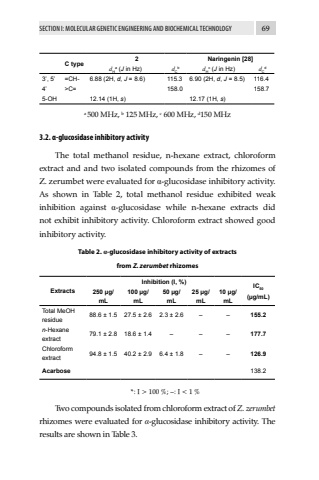
SECTION I: MOLECULAR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY 69C type2 Naringenin [28]dHa (J in Hz) dCb dHc (J in Hz) dCd3%u2019, 5%u2019 =CH- 6.88 (2H, d, J = 8.6) 115.3 6.90 (2H, d, J = 8.5) 116.44%u2019 >C= 158.0 158.75-OH 12.14 (1H, s) 12.17 (1H, s)a 500 MHz, b 125 MHz, c 600 MHz, d150 MHz3.2. %u03b1-glucosidase inhibitory activity The total methanol residue, n-hexane extract, chloroform extract and and two isolated compounds from the rhizomes of Z. zerumbet were evaluated for %u03b1-glucosidase inhibitory activity. As shown in Table 2, total methanol residue exhibited weak inhibition against %u03b1-glucosidase while n-hexane extracts did not exhibit inhibitory activity. Chloroform extract showed good inhibitory activity.Table 2. %u03b1-glucosidase inhibitory activity of extracts from Z. zerumbetrhizomesExtractsInhibition (I, %) IC50(%u00b5g/mL) 250 %u00b5g/mL100 %u00b5g/mL50 %u00b5g/mL25 %u00b5g/mL10 %u00b5g/mLTotal MeOH residue 88.6 %u00b1 1.5 27.5 %u00b1 2.6 2.3 %u00b1 2.6 %u2013 %u2013 155.2n-Hexane extract79.1 %u00b1 2.8 18.6 %u00b1 1.4 %u2013 %u2013 %u2013 177.7Chloroformextract94.8 %u00b1 1.5 40.2 %u00b1 2.9 6.4 %u00b1 1.8 %u2013 %u2013 126.9Acarbose 138.2*: I > 100 %; %u2013: I < 1 %Two compounds isolated from chloroform extract of Z. zerumbetrhizomes were evaluated for %u03b1-glucosidase inhibitory activity. The results are shown in Table 3.