Page 117 - Demo
P. 117
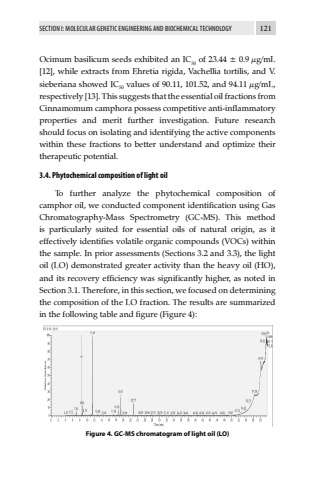
SECTION I: MOLECULAR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY 121Ocimum basilicum seeds exhibited an IC50 of 23.44 %u00b1 0.9 %u00b5g/mL [12], while extracts from Ehretia rigida, Vachellia tortilis, and V. sieberiana showed IC50 values of 90.11, 101.52, and 94.11 %u00b5g/mL, respectively [13]. This suggests that the essential oil fractions from Cinnamomum camphora possess competitive anti-inflammatory properties and merit further investigation. Future research should focus on isolating and identifying the active components within these fractions to better understand and optimize their therapeutic potential.3.4. Phytochemical composition of light oilTo further analyze the phytochemical composition of camphor oil, we conducted component identification using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). This method is particularly suited for essential oils of natural origin, as it effectively identifies volatile organic compounds (VOCs) within the sample. In prior assessments (Sections 3.2 and 3.3), the light oil (LO) demonstrated greater activity than the heavy oil (HO), and its recovery efficiency was significantly higher, as noted in Section 3.1. Therefore, in this section, we focused on determining the composition of the LO fraction. The results are summarized in the following table and figure (Figure 4):Figure 4. GC-MS chromatogram of light oil (LO)