Page 494 - Ebook HTKH 2024
P. 494
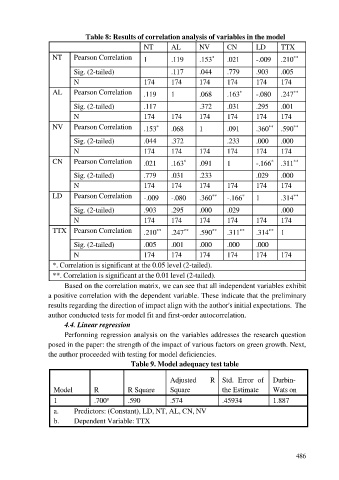
Table 8: Results of correlation analysis of variables in the model
NT AL NV CN LD TTX
NT Pearson Correlation 1 .119 .153 .021 -.009 .210
*
**
Sig. (2-tailed) .117 .044 .779 .903 .005
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
AL Pearson Correlation .119 1 .068 .163 -.080 .247
*
**
Sig. (2-tailed) .117 .372 .031 .295 .001
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
NV Pearson Correlation .153 .068 1 .091 .360 .590
*
**
**
Sig. (2-tailed) .044 .372 .233 .000 .000
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
CN Pearson Correlation .021 .163 .091 1 -.166 .311
*
**
*
Sig. (2-tailed) .779 .031 .233 .029 .000
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
LD Pearson Correlation -.009 -.080 .360 -.166 1 .314
**
*
**
Sig. (2-tailed) .903 .295 .000 .029 .000
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
TTX Pearson Correlation .210 .247 .590 .311 .314 1
**
**
**
**
**
Sig. (2-tailed) .005 .001 .000 .000 .000
N 174 174 174 174 174 174
*. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
Based on the correlation matrix, we can see that all independent variables exhibit
a positive correlation with the dependent variable. These indicate that the preliminary
results regarding the direction of impact align with the author's initial expectations. The
author conducted tests for model fit and first-order autocorrelation.
4.4. Linear regression
Performing regression analysis on the variables addresses the research question
posed in the paper: the strength of the impact of various factors on green growth. Next,
the author proceeded with testing for model deficiencies.
Table 9. Model adequacy test table
Adjusted R Std. Error of Durbin-
Model R R Square Square the Estimate Wats on
1 .700 .590 .574 .45934 1.887
a
a. Predictors: (Constant), LD, NT, AL, CN, NV
b. Dependent Variable: TTX
486