Page 95 - Demo
P. 95
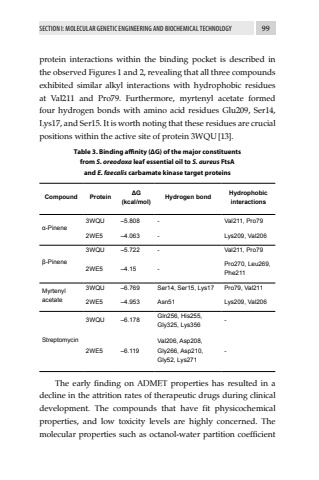
SECTION I: MOLECULAR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY 99protein interactions within the binding pocket is described in the observed Figures 1 and 2, revealing that all three compounds exhibited similar alkyl interactions with hydrophobic residues at Val211 and Pro79. Furthermore, myrtenyl acetate formed four hydrogen bonds with amino acid residues Glu209, Ser14, Lys17, and Ser15. It is worth noting that these residues are crucial positions within the active site of protein 3WQU[13].Table 3. Binding affinity (%u0394G) of the major constituents from S. oreodoxa leaf essential oil to S. aureus FtsA and E. faecalis carbamate kinase target proteinsCompound Protein %u0394G (kcal/mol) Hydrogen bond Hydrophobic interactions%u03b1-Pinene3WQU %u20135.808 - Val211, Pro792WE5 %u20134.063 - Lys209, Val206%u03b2-Pinene3WQU %u20135.722 - Val211, Pro792WE5 %u20134.15 - Pro270, Leu269, Phe211Myrtenyl acetate3WQU %u20136.769 Ser14, Ser15, Lys17 Pro79, Val2112WE5 %u20134.953 Asn51 Lys209, Val206Streptomycin3WQU %u20136.178 Gln256, His255, Gly325, Lys356 -2WE5 %u20136.119Val206, Asp208, Gly266, Asp210, Gly52, Lys271-The early finding on ADMET properties has resulted in a decline in the attrition rates of therapeutic drugs during clinical development. The compounds that have fit physicochemical properties, and low toxicity levels are highly concerned. The molecular properties such as octanol-water partition coefficient