Page 387 - Ebook HTKH 2024
P. 387
an effective internal audit function regarding ESG which fulfills its competency 172
including professionalism, performance, environment, leadership, and communication.
2. Literature review
According to IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards (S1, S2) 173 , “ESG” stands
for “Environmental, Social and Governance”, which is a set of criteria used to evaluate
a company’s non-financial performance. ESG is a collective term for a business's impact
on the environment and society as well as how robust and transparent its governance is
in terms of company leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder
rights. It measures how your business integrates environmental, social, and governance
practices into operations, as well as your business model, its impact, and its
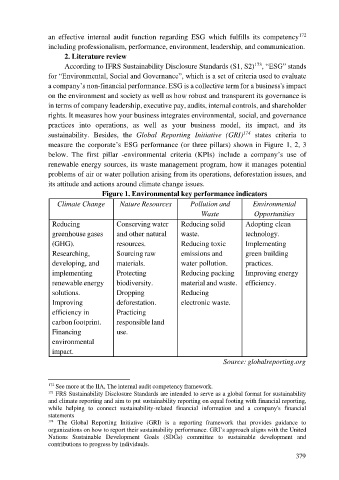
sustainability. Besides, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) 174 states criteria to
measure the corporate’s ESG performance (or three pillars) shown in Figure 1, 2, 3
below. The first pillar -environmental criteria (KPIs) include a company’s use of
renewable energy sources, its waste management program, how it manages potential
problems of air or water pollution arising from its operations, deforestation issues, and
its attitude and actions around climate change issues.
Figure 1. Environmental key performance indicators
Climate Change Nature Resources Pollution and Environmental
Waste Opportunities
Reducing Conserving water Reducing solid Adopting clean
greenhouse gases and other natural waste. technology.
(GHG). resources. Reducing toxic Implementing
Researching, Sourcing raw emissions and green building
developing, and materials. water pollution. practices.
implementing Protecting Reducing packing Improving energy
renewable energy biodiversity. material and waste. efficiency.
solutions. Dropping Reducing
Improving deforestation. electronic waste.
efficiency in Practicing
carbon footprint. responsible land
Financing use.
environmental
impact.
Source: globalreporting.org
172 See more at the IIA, The internal audit competency framework.
173 FRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards are intended to serve as a global format for sustainability
and climate reporting and aim to put sustainability reporting on equal footing with financial reporting,
while helping to connect sustainability-related financial information and a company's financial
statements
174 The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a reporting framework that provides guidance to
organizations on how to report their sustainability performance. GRI’s approach aligns with the United
Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) committee to sustainable development and
contributions to progress by individuals.
379