Page 27 - Demo
P. 27
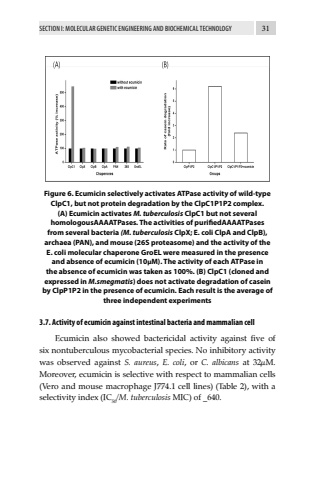
SECTION I: MOLECULAR GENETIC ENGINEERING AND BIOCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY 31Figure 6. Ecumicin selectively activates ATPase activity of wild-type ClpC1, but not protein degradation by the ClpC1P1P2 complex. (A) Ecumicin activates M. tuberculosis ClpC1 but not several homologousAAAATPases. The activities of purifiedAAAATPases from several bacteria (M. tuberculosis ClpX; E. coli ClpA and ClpB), archaea (PAN), and mouse (26S proteasome) and the activity of the E. coli molecular chaperone GroEL were measured in the presence and absence of ecumicin (10%u03bcM). The activity of each ATPase in the absence of ecumicin was taken as 100%. (B) ClpC1 (cloned and expressed in M.smegmatis) does not activate degradation of casein by ClpP1P2 in the presence of ecumicin. Each result is the average of three independent experiments 3.7. Activity of ecumicin against intestinal bacteria and mammalian cellEcumicin also showed bactericidal activity against five of six nontuberculous mycobacterial species. No inhibitory activity was observed against S. aureus, E. coli, or C. albicans at 32%u03bcM. Moreover, ecumicin is selective with respect to mammalian cells (Vero and mouse macrophage J774.1 cell lines) (Table 2), with a selectivity index (IC50/M. tuberculosis MIC) of _640.