Page 149 - Ebook HTKH 2024
P. 149
4.4. Moderating effect analysis
Before running the analysis, the data of global experience (age), cultural distance
(CUL), economic distance (ECO) and institutional distance (INS) is standardised by
the Descriptive statistics tool of SPSS. Given that global experience is considered as a
continuous variable, to test the moderating effects of this variable, we built the
interaction analysis model in AMOS 16. Following Hair et. al. (2005), the regressions
illustrated as flow with the interaction variables created by employing SPSS (namely:
CUL*AGE, ECO*AGE, INS*AGE)
PER = p1*LCD+p2*AGE+p3*(CUL*AGE)
PER = p1*ECO+p2*AGE+p3*(ECO*AGE)
PER = p1*INS + p2*AGE+p3*(INS*AGE)
The results confirm a significance for the moderating effects of global experience
on the three concerning relationships. In other words, the impacts of cultural distance,
economic distance and institutional distance on international subsidiaries are moderated
by global experience. The detailed result is illustrated through table 2.
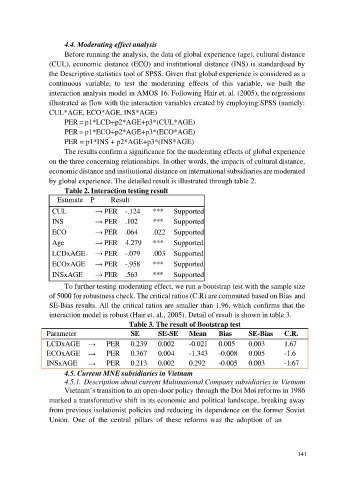
Table 2. Interaction testing result
Estimate P Result
CUL → PER -.124 *** Supported
INS → PER .102 *** Supported
ECO → PER .064 .022 Supported
Age → PER 4.279 *** Supported
LCDxAGE → PER -.079 .003 Supported
ECOxAGE → PER -.958 *** Supported
INSxAGE → PER .563 *** Supported
To further testing moderating effect, we run a bootstrap test with the sample size
of 5000 for robustness check. The critical ratios (C.R) are commuted based on Bias and
SE-Bias results. All the critical ratios are smaller than 1.96, which confirms that the
interaction model is robust (Hair et. al., 2005). Detail of result is shown in table 3.
Table 3. The result of Bootstrap test
Parameter SE SE-SE Mean Bias SE-Bias C.R.
LCDxAGE → PER 0.239 0.002 -0.021 0.005 0.003 1.67
ECOxAGE → PER 0.367 0.004 -1.343 -0.008 0.005 -1.6
INSxAGE → PER 0.213 0.002 0.292 -0.005 0.003 -1.67
4.5. Current MNE subsidiaries in Vietnam
4.5.1. Description about current Multinational Company subsidiaries in Vietnam
Vietnam’s transition to an open-door policy through the Doi Moi reforms in 1986
marked a transformative shift in its economic and political landscape, breaking away
from previous isolationist policies and reducing its dependence on the former Soviet
Union. One of the central pillars of these reforms was the adoption of an
141